SPM Biology 15 Variation (Part 2)
Mutation
Mutation is a spontaneous change in genetic composition of a cell. It can occur in somatic cells or gametes.
Mutation is caused by:
Gene mutation involves changes to the bases in the DNA of one gene. For example:
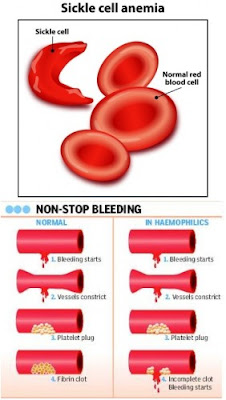
- sickle cell anemia (mutation to gene that causes red blood cells to become sickle-shaped).
- albinism (mutation to gene that control the production of melanin pigment).
- haemophilia.
 |
| Gene mutation |
Chromosomal Mutation
Changes in the structure or the number of chromosomes are called chromosomal mutation. Examples of the alterations in the structure of some parts of the chromosome are duplication, deletion, translocation and inversion. Chromosomal mutation can happen during mitosis and meiosis when chromosomes are condensed and pulled apart. It also occurs during crossing over.
 |
| Chromosomal Mutation |
Mutagens are the substances that can also cause the mutation or increase the rate of mutation. For instance:
- x-ray
- ultraviolet radiation
- chemical substances such as nitrous acid, formaldehyde, food preservatives, pesticides, drugs and some components in cigarette smoke.

No comments:
Post a Comment