Enzymes
(a biological catalyst that increases rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed during the reaction)
1. Enzymology: the study of enzymes.2. Enzymes are protein!!3. Act as biological catalysts (speed up biochemical reactions in the cell but remain unchanged at the end of the reactions).
4. The molecules which react in the enzyme-catalyzed reaction are called substrates. The molecules produced at the end of the reaction are called products.
 |
| Enzyme-catalyzed reaction |
6. Enzymes are synthesized by ribosomes.
General Characteristics of Enzymes
- Enzymes speed up the rate of biochemical reactions.
- Enzymes are not destroyed by the reactions which they catalyze.
- Enzymes are effective in small amount.
- Enzymes can work in either direction.
- Enzymes are denatured by high temperatures.
- Enzymes are sensitive to pH.
- Enzymes are extremely specific.
- Enzyme activity is affected by inhibitors.
- Some enzymes require co-factors.
Mechanism of Enzyme Reaction
 |
| Mechanism of enzyme reaction |
Lock and Key Hypothesis
1. Enzymes are specific.
2. Any change in the shape of an enzymes alters it effectiveness.
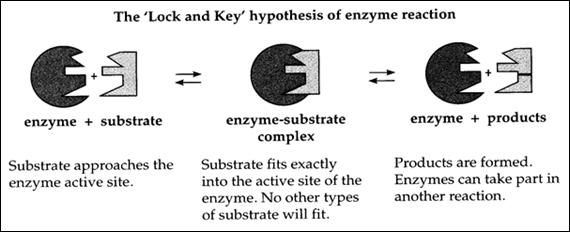 |
| Lock and Key hypothesis |
Factors Affecting the Activity of Enzymes
- pH
- temperature
- enzyme concentration on enzyme activity
- substrate concentration on enzyme activity
 |
| The optimum pH of some enzymes |
2. temperature
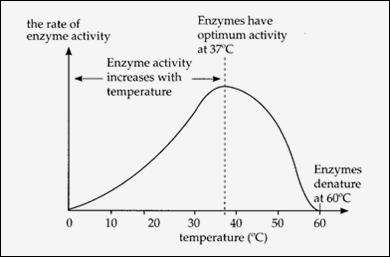 |
| Enzymes have optimum activity at 37°C |
3. enzyme concentration on enzyme activity
- Enzyme activity increases with enzyme concentration until the number of substrates becomes the limiting factor.
 |
| Enzyme concentration on enzyme activity |
4. substrate concentration on enzyme activity
- Enzyme activity increases with substrate concentration until the number of enzymes becomes the limiting factor.
 |
| Substrate concentration on enzyme activity |
thanks for the information and posts
ReplyDeletenuzymes